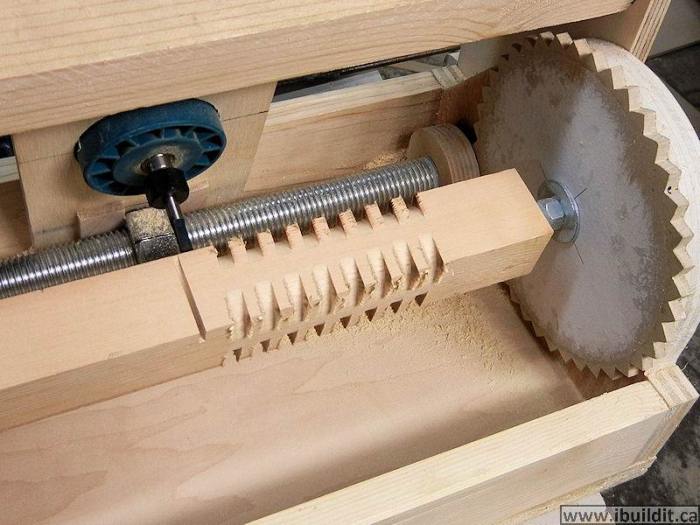
Create Threads on Steel Rod Using Die Set is a crucial skill for various industries, from automotive to aerospace. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process, covering everything from choosing the right die set to ensuring optimal thread quality. We’ll delve into different types of die sets, essential tools, and safety precautions to help you master this technique.
Understanding the intricacies of die threading is essential for precision manufacturing. This detailed guide explores the fundamental principles and step-by-step procedures, empowering you to create flawless threads on steel rods.
Introduction to Threading Steel Rods with Die Sets
Creating threads on steel rods is a crucial process in various manufacturing and mechanical applications. This process ensures precise connections and allows components to be assembled securely. Die sets are the primary tools used for this purpose, providing a reliable and efficient method for achieving consistent thread profiles.The process of threading involves shaping the rod’s surface to create a helical groove, known as a thread.
Die sets accomplish this by utilizing hardened steel dies that are precisely shaped to match the desired thread form. These dies are designed to accommodate different thread sizes and pitches, making them versatile tools for a wide range of applications.
Types of Die Sets
Different types of die sets are available, each suited for specific thread sizes, materials, and thread forms. The selection of a die set is critical to ensure a high-quality thread and avoid damaging the rod or the die set itself. Standard die sets are available for common thread sizes, while specialized die sets are designed for uncommon or complex thread forms.
Fundamental Principles of Die Threading
The die-threading process relies on the principle of progressive deformation. The rod material is gradually compressed and shaped within the die, forming the desired helical thread. Proper lubrication is essential to reduce friction between the rod and the die, preventing excessive wear and ensuring a smooth threading operation. The die set’s design, including the angle and shape of the die’s cutting edges, is critical in determining the quality and consistency of the thread.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Die Threading
A typical die-threading procedure involves these steps:
- Preparation: Ensure the steel rod is clean and free of any burrs or imperfections. Lubricate the rod with a suitable lubricant to reduce friction during the threading process. Select the appropriate die set based on the desired thread size and material of the rod.
- Die Set Assembly: Carefully assemble the die set according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure all components are properly aligned and secure. Incorrect assembly can lead to damaged dies or an improperly formed thread.
- Threading: Position the rod in the die set and apply a controlled and consistent force to advance the rod through the dies. Consistent pressure and a steady feed rate are crucial to ensure a high-quality thread. Using a threading machine or a manual threading tool can enhance efficiency and control.
- Inspection: After the threading process, inspect the thread for any imperfections. This includes checking for burrs, inconsistent thread depth, or damage to the thread profile. Measuring the thread pitch and diameter ensures conformance to the specifications. Any imperfections should be addressed before proceeding to further assembly.
Material Compatibility and Selection
Different materials require different die sets to avoid damage to the dies and the rod itself. The hardness of the material will affect the die’s ability to create the thread. Using a die set that is not compatible with the material can result in premature wear of the dies and create an uneven thread. Choosing a die set made from high-quality steel is essential for achieving the best results.
Types of Die Sets and Their Applications
Die sets are essential tools for creating threads on steel rods, and their effectiveness depends heavily on the type of die set used. Understanding the different types available, their applications, and the specific industries they support is crucial for selecting the right tool for a given job. This exploration will delve into the distinctions between single-die, multiple-die, and automatic die sets, highlighting their unique strengths and weaknesses.Different die set types cater to various needs, from simple threading tasks to high-volume production.
Each design offers a specific advantage, and understanding these nuances allows for optimal selection based on the project requirements. This knowledge also aids in identifying the most suitable set for repair and maintenance procedures in different industrial settings.
Single-Die Sets
Single-die sets are the most basic type, consisting of a single die that threads the rod. They are typically used for smaller-scale projects or repair work where the required thread length is limited.
Multiple-Die Sets
Multiple-die sets, in contrast, employ multiple dies, each responsible for a different stage of the threading process. This approach is beneficial for projects demanding more complex threads or when the rod length requires multiple passes for precise threading.
Automatic Die Sets
Automatic die sets automate the entire threading process, reducing the need for manual intervention. These sets are particularly well-suited for high-volume manufacturing, where speed and consistency are paramount.
Applications in Various Industries
- Manufacturing: In automotive manufacturing, single-die sets can be used for threading smaller components, while multiple-die sets are crucial for creating complex threads on engine parts. Automatic die sets are prevalent in high-volume production lines for mass-produced fasteners and components.
- Repair and Maintenance: Single-die sets are often used for repair work, such as threading bolts or rods in equipment maintenance. Multiple-die sets are valuable in repairing complex machinery components requiring precise threading. Automatic die sets are rarely employed in repair settings due to their high cost and complexity.
- Other Industries: Die threading is also common in industries like construction (for threading reinforcing rods), aerospace (for precise threading on aircraft components), and the oil and gas sector (for threading pipelines and other equipment).
Comparison of Die Set Types
| Feature | Single-Die | Multiple-Die | Automatic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lowest | Medium | Highest |
| Speed | Slowest | Medium | Fastest |
| Complexity | Simplest | Intermediate | Most Complex |
| Accuracy | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Applications | Small-scale, repair | Complex threading, medium volume | High volume, mass production |
Die set selection is critical to ensure efficiency and quality in threading operations. Considering the project scale, complexity, and desired output speed will help determine the ideal die set type.
Materials and Tools for Die Threading

Choosing the right materials and tools is crucial for successful die threading. Incorrect material selection can lead to premature tool wear, inconsistent threads, and ultimately, a failed project. Similarly, inadequate tool maintenance compromises efficiency and precision. This section details the critical components for a smooth and effective die threading process.
Creating threads on steel rods using a die set is a crucial skill in metalworking. It’s all about precision and getting the right finish, which is why I’ve been spending a lot of time perfecting the technique. While I’m immersed in this process, I’ve been enjoying listening to Thurston Moore’s new song, listen to thurston moores new song cease fire , which is oddly inspiring for such a meticulous task.
Hopefully, this focused listening won’t distract me from my next project, a complex thread on a high-strength steel rod.
Common Steel Rod Materials
Selecting the appropriate steel rod material directly impacts the thread’s quality and longevity. Different grades of steel exhibit varying degrees of hardness, tensile strength, and ductility, affecting the threading process. The most commonly used materials for die threading include:
- Carbon Steel: A cost-effective option, carbon steel rods are readily available and suitable for applications requiring moderate strength and durability. However, their susceptibility to corrosion requires careful consideration in exposed environments.
- Alloy Steel: Alloy steel rods, containing elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, offer enhanced strength, hardness, and resistance to wear compared to carbon steel. This makes them ideal for applications demanding higher tolerances and longevity.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel rods are highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, making them perfect for outdoor or corrosive environments. Their higher cost and potentially more complex threading processes should be factored in during material selection.
Essential Die Threading Tools
A comprehensive set of tools is essential for achieving accurate and consistent threads. These tools include:
- Die Sets: The die set, comprising a series of dies of progressively smaller diameters, forms the threads. Proper die selection is vital for the desired thread profile and ensures efficient material flow. The dies must match the thread size and type for optimal performance.
- Die Holders: These holders securely grip the dies and maintain the correct alignment for accurate threading. Their quality significantly influences the consistency and precision of the thread.
- Steel Rod: The steel rod itself, as mentioned, must be the correct material and dimension for the die set to work effectively. The rod’s condition—whether it’s cold-drawn or hot-rolled—can impact the threading process.
- Lubricant: Lubrication is essential for minimizing friction during the threading process, reducing wear on both the dies and the rod. Lubricants such as oil or grease effectively prevent damage.
- Safety Equipment: Safety glasses, gloves, and potentially a respirator are critical for preventing injuries during the threading process. These are essential for protecting against flying particles and potential hazards.
Importance of Material Selection and Tool Maintenance
Choosing the right steel rod material and ensuring proper maintenance of the die threading tools is crucial for successful results. Incorrect material selection can result in thread stripping, uneven threads, or premature tool wear. Regular maintenance of the dies, including cleaning and proper storage, extends their lifespan and guarantees consistent performance.
Lubrication During the Threading Process
Lubrication plays a significant role in the die threading process. Proper lubrication reduces friction, prevents galling, and significantly prolongs the life of both the dies and the rod. Applying a suitable lubricant, such as oil or grease, throughout the threading operation minimizes wear and ensures smooth operation. Using excessive lubricant may cause a buildup that affects the die threading process.
Proper lubricant application is essential for a successful and efficient die threading operation.
Procedure and Techniques for Creating Threads
Creating threads on steel rods using a die set is a crucial process in various manufacturing and repair applications. Understanding the proper procedure, alignment, and pressure application is paramount to achieving consistent and high-quality threads. This section will delve into the detailed steps involved, emphasizing the importance of these factors and presenting different techniques, both manual and automated.Proper threading ensures the longevity and reliability of mechanical components, avoiding premature wear and tear.
Accuracy in thread creation is critical for the proper functioning of interconnected parts. Consistent thread profiles guarantee optimal engagement and prevent slippage or damage.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Creating Threads
This procedure Artikels the typical steps involved in creating threads using a die set. Accurate execution of each step is vital for producing threads with consistent quality.
- Preparation: Ensure the steel rod is clean and free of any burrs or imperfections. This will prevent issues during the threading process and ensure a smooth finish.
- Die Set Selection: Choose the correct die set based on the desired thread size and type. Using the wrong die set can lead to incorrect thread dimensions and damage the rod or die.
- Die Set Alignment: Precise alignment of the dies is critical. Misalignment can result in uneven threads and potentially damage the rod or the die set itself. Ensure the dies are correctly positioned and secured in the die holder. This often involves tightening the adjusting screws or clamps on the die holder.
- Rod Positioning: Carefully position the steel rod in the die holder, ensuring it’s centered and aligned with the die set.
- Application of Pressure: Apply consistent and controlled pressure to the rod. Excessive pressure can deform the rod, while insufficient pressure will not effectively cut the thread. The pressure needed often depends on the material hardness and die set.
- Threading Process: Rotate the rod slowly and consistently through the die set. Ensure continuous contact between the rod and the dies. Do not force the rod if resistance is encountered. This may indicate a problem with alignment or the die set itself.
- Inspection: Inspect the threads after each pass. Ensure that the threads are consistent in size, shape, and pitch. Visually check for burrs or imperfections. If any problems are detected, address them before proceeding to the next pass.
Importance of Alignment and Pressure
Precise alignment of the die set and controlled pressure application are paramount for achieving consistent thread quality.
- Alignment: Proper alignment ensures that the dies cut the rod uniformly, resulting in consistent thread dimensions. Misalignment can lead to uneven threads, burrs, and damage to the rod or die set. Visual inspection before and during the threading process can help identify and correct alignment issues.
- Pressure: The correct pressure application is critical to avoid damaging the rod or the dies. Excessive pressure can deform the rod, while insufficient pressure will not effectively cut the thread. Adjust the pressure according to the material properties of the steel rod and the die set design. Monitoring the pressure throughout the process is important.
Techniques for Threading Steel Rods
Different techniques are available for creating threads, catering to varying needs and production scales.
- Manual Methods: Manual threading using a hand-operated die set is suitable for smaller-scale projects or situations where automated solutions are unavailable. Careful application of pressure and consistent rotation of the rod are essential. Experience is crucial in achieving consistent threads.
- Automated Methods: Automated systems, such as threading machines, are widely used for high-volume production. These machines provide consistent pressure and rotation, resulting in higher efficiency and improved thread quality. Modern automated systems often incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms to maintain precise thread dimensions and prevent damage.
Adjusting Die Sets for Optimal Results
Proper adjustment of the die set is crucial for achieving optimal results. Incorrect adjustment can lead to inconsistent threads and damage to the dies or the rod.
Creating threads on steel rods using a die set is a crucial manufacturing process. Speaking of cool giveaways, did you hear the Chicago White Sox are giving away Disco Demolition Night t-shirts for their 40th anniversary? This awesome promotion is a blast from the past, but back to the task at hand. Proper die set selection and precise operation are key to successful thread creation, ensuring a strong and reliable finished product.
- Die Set Adjustment: Die sets often include mechanisms for adjusting the gap between the dies. Proper adjustment of the gap ensures that the dies cut the rod with the correct thread profile. Following the manufacturer’s instructions is crucial.
- Checking for Wear: Regularly inspect the dies for wear and tear. Worn dies can produce inconsistent threads. Replacement of worn dies is necessary to maintain quality.
Quality Control and Troubleshooting: Create Threads On Steel Rod Using Die Set
Achieving consistent and high-quality threads when using a die set is crucial for the longevity and performance of the final product. Thorough quality control measures prevent costly errors and ensure the thread meets the specified standards. This section details the importance of inspection, common issues, and their solutions to maintain the precision of the threading process.
Importance of Quality Control
Maintaining consistent thread quality is paramount in manufacturing. Variations in thread dimensions or form can lead to issues like poor fit, premature failure, or even safety hazards in assembled components. Regular inspections and adherence to established standards guarantee that the threads meet the required tolerances, ensuring proper functionality and longevity. Implementing quality control protocols saves time and resources by identifying and rectifying issues early in the process.
Inspection Methods for Thread Defects
Proper inspection techniques are essential to identify and address potential problems. Visual inspection is the first step, checking for obvious defects such as burrs, cracks, or misaligned threads. A calibrated micrometer or thread gauge allows for precise measurement of thread dimensions, confirming that they fall within the specified tolerances. Using a thread pitch gauge helps determine if the thread’s pitch (distance between threads) is accurate.
These methods, when combined, provide a comprehensive evaluation of the thread quality.
Common Problems and Solutions
Troubleshooting during die threading is an integral part of the process. A list of common issues and their corresponding solutions is provided below.
- Incorrect Die Selection: Using the wrong die set for the specific thread size or material can lead to poor quality threads. Careful selection of the correct die set based on the thread specifications is critical. Consulting the manufacturer’s specifications for the correct die set for the intended thread is essential.
- Die Wear: Die sets, like any tool, can wear out over time. Significant wear can result in inconsistent threads and dimensions. Regularly checking the condition of the dies and replacing them when necessary is crucial for maintaining quality. This helps ensure the threads conform to the required standards. Replacement is recommended when the dies show signs of significant wear or when inconsistencies in the thread quality are detected.
- Improper Die Lubrication: Insufficient lubrication during threading can cause friction, leading to inconsistent thread profiles. Proper lubrication helps to reduce friction, improve die life, and produce smoother threads. Choosing the appropriate lubricant for the specific material is crucial.
- Incorrect Rod Preparation: A poorly prepared rod can affect the quality of the final thread. Ensuring the rod is clean, straight, and free from defects before threading is essential. Rods with burrs or imperfections will result in threads with inconsistencies and may cause damage to the die.
- Improper Die Setting: Misalignment of the die set can cause inconsistent threads. Correct die setting ensures proper contact with the rod, leading to consistent thread formation. Checking the alignment of the die set before starting the threading process is crucial.
Identifying and Correcting Thread Consistency and Dimensional Issues
Maintaining thread consistency and dimensional accuracy is crucial for achieving the desired outcome. Inconsistencies can arise from various factors, including incorrect die selection, material properties, or die wear. A thorough examination of the process, using appropriate tools, helps identify the root cause. Correcting inconsistencies often involves replacing worn dies, adjusting the die setting, or re-evaluating the material specifications.
Regular calibration of the measuring tools is also important. Consistent monitoring and adjustments to the process can prevent major quality issues and keep the output consistent.
Troubleshooting Thread Consistency
Consistency in thread form and dimensions is vital for the proper functioning of components. A thread with uneven pitches or inconsistent depth may lead to improper fit or malfunction. To rectify this, thorough inspections using calibrated thread gauges are essential. This process ensures the thread dimensions meet the required specifications, improving product reliability.
Safety Precautions and Considerations

Creating threads on steel rods using die sets is a crucial manufacturing process, but it’s essential to prioritize safety throughout the procedure. Ignoring safety precautions can lead to serious injuries, equipment damage, and even fatalities. This section Artikels the vital safety measures and considerations to ensure a secure and productive work environment.
Creating threads on steel rods using a die set is a precise process, requiring careful attention to detail. It’s similar to the intricate lyrical battles between rappers, like the one Pusha T had with Drake, as discussed in this fascinating Breakfast Club interview pusha t discusses drake diss on the breakfast club listen. Ultimately, both require a lot of skill and precision to achieve the desired outcome, whether it’s a perfectly threaded rod or a devastating diss track.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount during die threading. It forms the first line of defense against potential hazards. Failure to wear appropriate PPE can significantly increase the risk of injury.
- Eye Protection: Safety glasses or face shields are critical to protect the eyes from flying debris, metal chips, and potential sparks generated during the die threading process. Examples include impact-resistant safety glasses or full-face shields with side protection, specifically designed for industrial applications. Choosing the appropriate type depends on the specific hazards involved.
- Hand Protection: Gloves, preferably made of leather or a similar material, are essential to protect hands from cuts, abrasions, and potential chemical exposure. Heavy-duty work gloves are often necessary to prevent injury while handling the steel rod and the die set.
- Hearing Protection: Die threading operations often involve high-speed rotations or hammering. Workers should wear earplugs or earmuffs to protect their hearing from potential noise-induced damage. The intensity of noise should be considered when choosing the appropriate hearing protection.
- Foot Protection: Steel-toe safety shoes or boots are required to protect feet from falling objects, sharp edges, and potential impacts. Choosing footwear appropriate for the working environment, considering potential slip hazards, is important.
Potential Hazards of Die Threading, Create Threads on Steel Rod Using Die Set
Die threading presents several hazards that necessitate proactive safety measures. Understanding these hazards is crucial to implementing effective preventative measures.
- Flying Debris: During the die threading process, metal chips and particles can be ejected at high speeds, posing a significant risk to the eyes and other exposed body parts. The velocity and direction of the flying debris depend on the material, die set type, and machine settings.
- Noise Exposure: The machinery involved in die threading can produce considerable noise, potentially causing hearing damage if proper protection is not used. The level of noise exposure can vary based on the specific machine and the operating parameters.
- Material Handling Hazards: Handling steel rods and other materials can result in cuts, bruises, or other physical injuries. Proper lifting techniques and the use of appropriate handling tools can mitigate this risk.
- Equipment Malfunction: Equipment malfunctions during die threading operations can lead to serious injuries. Regular maintenance and safety checks are essential to prevent these incidents.
Workplace Safety Regulations and Guidelines
Adhering to workplace safety regulations and guidelines is crucial to ensure a safe environment for all workers involved in die threading.
- Machine Safety: Proper machine guarding and safety interlocks are vital. Any machine malfunction should be immediately reported and corrected by authorized personnel.
- Emergency Procedures: Clear and well-practiced emergency procedures should be in place in case of accidents. These procedures should include the location of emergency exits, first aid facilities, and emergency contacts.
- Regular Training: Regular training on safety procedures and equipment operation is essential to keep employees up-to-date on best practices. This includes training on hazard identification and risk assessment.
- Reporting Procedures: Establish clear procedures for reporting any incidents or near misses. This allows for the identification of potential hazards and implementation of corrective actions to prevent future incidents.
Examples of Die Threading Applications
Die threading, a precision machining process, plays a critical role in numerous industries. From the intricate components of aerospace vehicles to the robust structures of construction projects, die threading ensures the reliable connection and functionality of parts. This process, employing specialized die sets, guarantees consistent thread profiles and dimensions, crucial for the performance and safety of the end products.The precision achievable with die threading is vital in applications where consistent thread engagement and load-bearing capabilities are paramount.
This precision is often critical in high-stress environments, like those found in automotive and aerospace components. Different die set types are tailored to specific thread sizes and materials, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Automotive Applications
Die threading is extensively used in automotive manufacturing for a variety of components. The process ensures the accurate creation of threads on bolts, studs, and various other fasteners. This precision is essential for ensuring the reliable fastening of engine components, transmission parts, and chassis assemblies. The use of die sets allows for consistent thread engagement, vital for the structural integrity and longevity of the vehicle.
Furthermore, the ability to create multiple threads within a single component is often used in engine blocks and cylinder heads.
Aerospace Applications
In the demanding aerospace industry, die threading is indispensable for producing high-precision components. The intricate threads on fasteners, fittings, and other crucial parts demand the consistency and accuracy that die sets provide. For example, engine components and control systems require precise threading for optimal performance and safety. The consistent thread profiles produced by die sets are critical in maintaining the integrity and reliability of aircraft systems under extreme conditions.
This precision is crucial for the structural integrity of the aircraft and for ensuring the safety of passengers and crew.
Construction Applications
The construction industry relies on die threading for a variety of tasks. For example, pipe connections, anchoring systems, and specialized hardware often require precisely threaded components. The ability to create consistent threads on pipes and fittings is crucial for water supply, drainage, and other plumbing systems. Furthermore, the accurate threading of anchors and other structural components ensures the stability and safety of buildings and other structures.
Table of Examples
| Application | Industry | Die Set Type | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Bolt Threading | Automotive | Metric/Inch Die Set | Ensures secure fastening, precise dimensions, and consistent load-bearing capacity |
| Aircraft Fitting Connections | Aerospace | Fine Pitch Die Set | High precision for tight tolerances, ensuring structural integrity under extreme conditions |
| Pipe Coupling Threading | Construction | Pipe Die Set | Consistent thread profile for leak-proof connections, crucial in plumbing and other piping systems |
| Structural Anchor Threading | Construction | Heavy Duty Die Set | Robust threading for high-strength applications, ensuring stability and safety in building structures |
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
Mastering the art of die threading goes beyond basic procedures. Advanced techniques unlock the ability to create specialized threads, ensuring precision and meeting stringent requirements. Understanding die head applications, thread specifications, and the nuances of various rod materials and diameters is crucial for achieving optimal results.Specialized thread forms, like Acme, Buttress, and Square threads, demand specific die sets.
These specialized thread forms often exhibit unique characteristics, like high load-bearing capabilities or self-locking properties. Choosing the appropriate die set is essential for successful threading in these cases.
Specialized Thread Forms
Different thread forms cater to diverse applications. Understanding their characteristics allows for informed selection and application. Acme threads, known for their high load-carrying capacity, are frequently used in power screws and lead screws. Buttress threads, with their angled sides, are employed where high tensile strength is paramount. Square threads offer a balance of strength and self-locking characteristics.
Die Heads and Specialized Tools
Die heads are crucial components in advanced die threading. Different die head designs cater to diverse needs. For instance, some die heads are designed for threading complex shapes or large diameters, while others are optimized for threading multiple threads in a single operation. Specialized tools like die sets with adjustable dies or die head attachments for specific thread forms are also essential for precise threading.
Thread Specifications and Tolerances
Precise thread specifications are critical for ensuring compatibility and functionality. Tolerances define the acceptable variations in thread dimensions. Meeting these specifications is vital for ensuring the correct fit and function of threaded components. Strict adherence to standards, like ANSI (American National Standards Institute) or ISO (International Organization for Standardization), is essential for consistent quality. For example, a tolerance of ±0.005 inches on a 1/2-inch diameter thread ensures that the threads will properly engage with the mating parts.
Rod Diameter and Material Considerations
The diameter and material of the rod significantly influence the threading process. Larger diameters necessitate specialized die heads for effective threading. Different materials exhibit varying hardness and ductility, influencing the threading process. For instance, threading hardened steel rods requires more robust dies and potentially a different threading procedure compared to softer materials like aluminum. Aluminum may require lubrication during the process to prevent excessive friction.
Choosing the appropriate die set, lubricant, and threading speed is crucial for each material to avoid damage to the rod or the die set.
Safety Precautions
Safe practices are essential when working with die threading equipment. Ensure adequate ventilation and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) like safety glasses and gloves. Proper handling of dies and tools is crucial to prevent injuries. Following safety guidelines will reduce the risk of accidents. For instance, using appropriate lubrication to avoid excessive friction and heat buildup is a safety precaution.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, creating threads on steel rods using a die set involves careful selection of tools, precise procedures, and adherence to safety protocols. This comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge and techniques to confidently thread steel rods, ensuring quality and efficiency in your work. From basic procedures to advanced techniques, we’ve covered it all.